Blog Layout
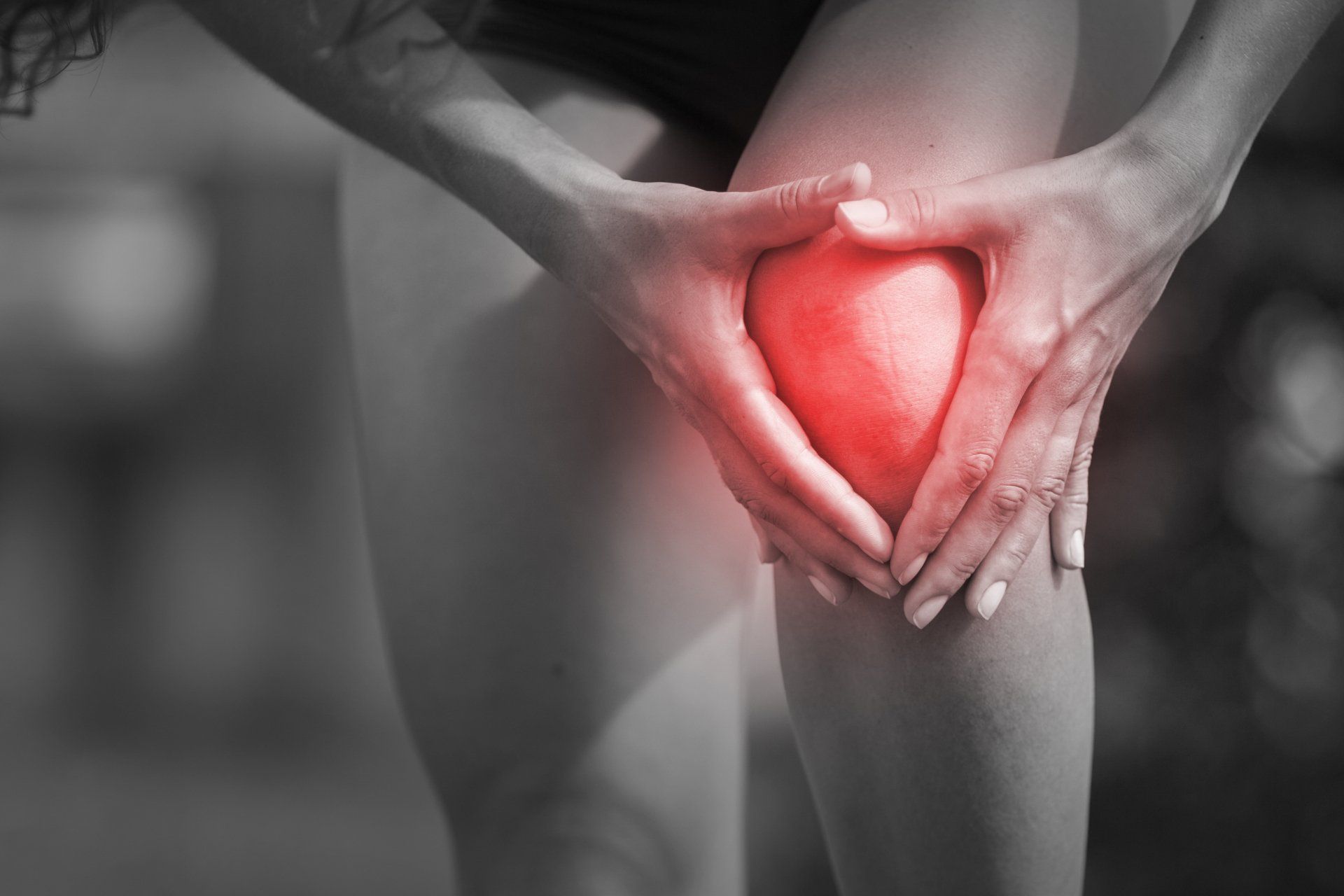
Runner's Knee
June 24, 2021
Runner’s Knee is one of the most common knee problems in sports, and can occur at any age. Runner’s knee is the softening of the cartilage on the kneecap, and roughening of the cartilage under the kneecap as a result of it not tracking properly. A proper shoe or insole can prevent lower extremity problems due to faulty biomechanics. Read on to learn more!
Symptoms
- Pain
- Along the medial (inner) aspect of the kneecap or just below the kneecap
- When using stairs or going up/down hills
- Worse after prolonged sitting with the knees bent
- More of a dull ache
- Cracking or grating in the knee
- Eventually, knee may want to “catch” and may feel like it wants to give out
Definitions
- Softening of the cartilage on the patella (kneecap)
- Roughening of the cartilage under the patella caused by the kneecap not tracking properly (patella does not glide smoothly over the femur/thigh bone)
- May also be referred to as Chondromalacia Patella
- One of the most common knee problems in running and other sports (may occur at any age)
Primary Cause
- Excessive Pronation
- Pronation is a normal movement of the foot, that allows the arch to flatten to a degree, which helps the body to absorb shock and adapt to different ground surfaces
- In analyzing ones gait, first contact is on the heel and outside of the foot, followed by a shift of bodyweight forward, toward the arch and toes
- If the foot is weak or tired and/or the footwear is not supportive, then the arch can flatten more than normal, which is excessive pronation
- Flattening of the arch (excessive pronation) increases stresses on the foot, which can further contribute to ankle, knee, hip and low back problems (a chain reaction)
- This repetitive, excessive pronation, is the main contributor to many lower extremity, overuse injuries
Contributing Factors
- Mechanical conditions including wide hips (females), knock knees, patella alta (high patella) and subluxating patella
- Over pronation of the foot
- Weakness of the quad, especially the VMO (Vastus Medialis Oblique Muscle) which runs along the inner aspect of the thigh and connects at the knee
- Overuse, or an increase in hill running or stair use
- Too large of a Q-angle at the knee (this is the angle of the quad muscle’s effective pull on the kneecap). Less than 12 degrees is normal and greater than 15 degrees is abnormal
Treatment
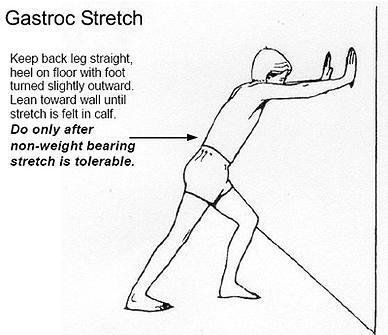
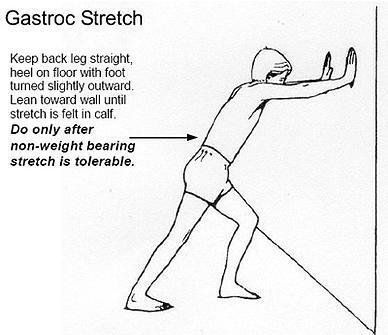
- The 3 S’s – Stretching, Strengthening and Supporting, along with ICE and REST, have been found to be the simplest and most effective treatment for these injuries.
- Stretching of the hamstring, quad, calf and IT Band with help to decrease pressure at the kneecap
- Strengthening of the quad, especially the VMO (vastus medialis oblique muscle) will help the kneecap to glide more correctly through the groove at the knee joint
- Supporting the foot with proper shoes and insoles, can prevent or help to eliminate the vast majority oflower extremity problems due to faulty biomechanics. This may be a Birkenstock sandal, with a broad base and contoured footbed, that is low to the ground and conforming to the foot. It may be a shoe with an upper that wraps the foot and supports the arch and heel thus limiting excessive pronation. The vast majority of footwear have more than enough cushion but very little support for the arch and heel. One ofthe easiest and most effective solutions is to add a simple over the counter insole that provides a forgivingsupport for both the arch and heel
- Avoid downhill running or going up/down stairs
- Avoid exercises done with the knee bent unless being done as an isometric
- Physical Therapy including exercise, ultrasound, iontophoresis and patellar mobilization
The following are a few helpful exercises. Check with your doctor for specifics on your condition and what you should or should not do for your problem.
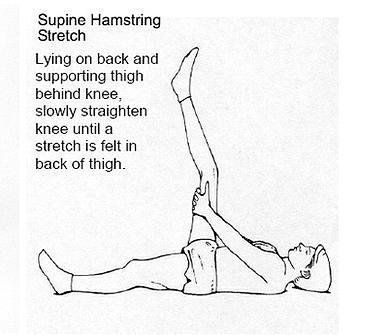
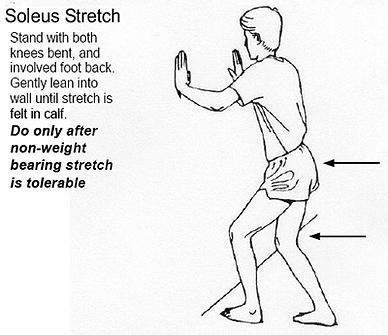
November 25, 2021
Pain in the Achilles Tendon can be caused by pronation, intense training or overuse, or poor support from your shoes. Finding a pair of shoes with good support on the inside of a shoe or in the shoe’s foundation/upper can ease the amount of stress placed on your foot and calf, thus preventing injury to the achilles tendon.
October 20, 2021
Pain in the Achilles Tendon can be caused by pronation, intense training or overuse, or poor support from your shoes. Finding a pair of shoes with good support on the inside of a shoe or in the shoe’s foundation/upper can ease the amount of stress placed on your foot and calf, thus preventing injury to the achilles tendon.
We are more than a traditional retail shoe store! Our goal is to fit our customers with the best shoe for their goals & lifestyle! Get fitted today!
Quick Links
Business Hours
Tue - Sat: 10am - 6pm
Sunday and Monday: Closed
Be the First to Know
Footer Form - Email Form
Thank you for contacting us.
We will get back to you as soon as possible.
We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Oops, there was an error sending your message.
Please try again later.
Please try again later.
The Foot Store
© 2025