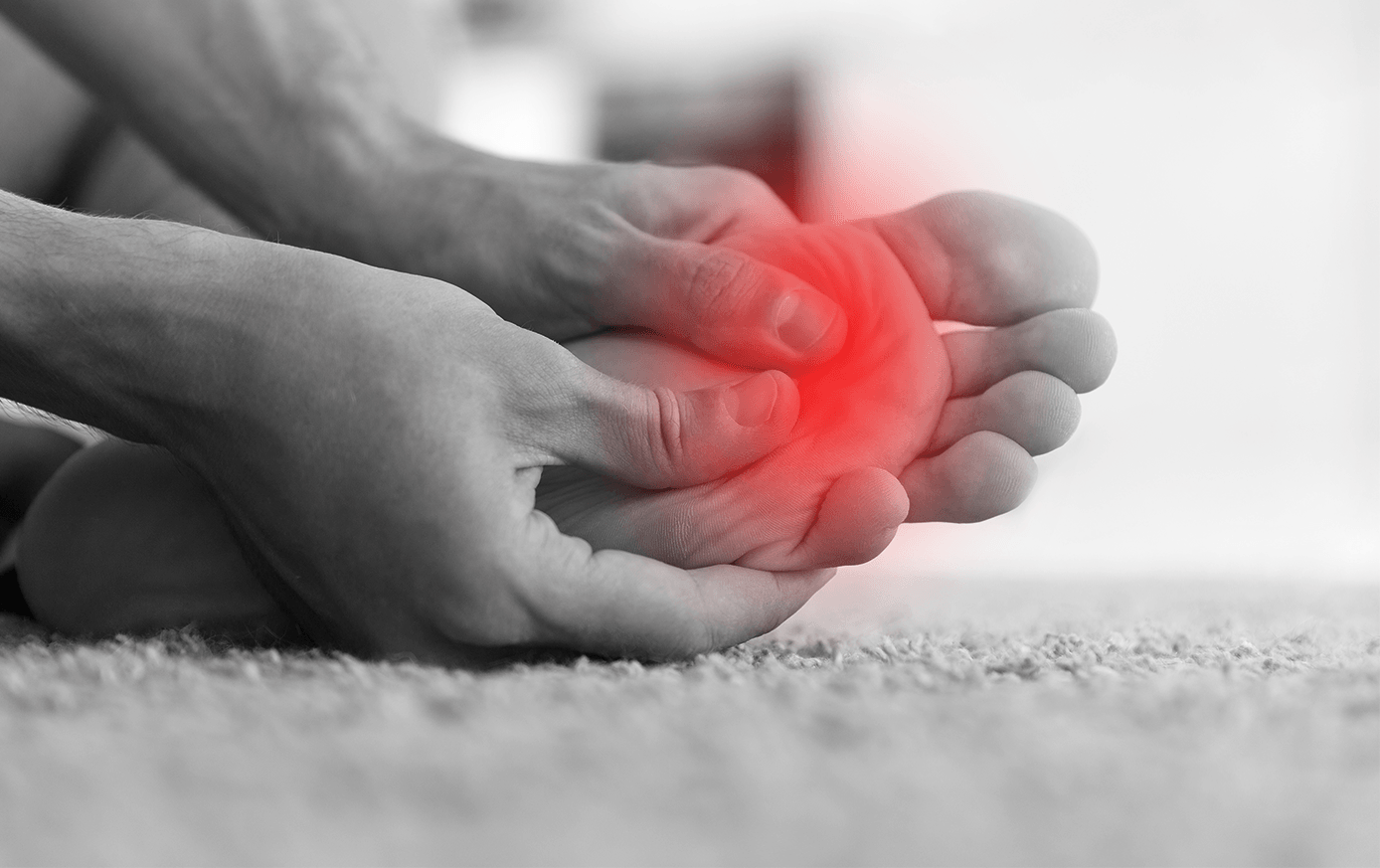
Neuromas
July 4, 2021
Neuromas are generally more common in adult females, and refer to an inflamed bundle of nerve endings that cause pain in the ball of the foot. Tight, poorly fitting shoes (like heels), are a common cause. Visit The Foot Store for supportive, proper fitting shoes to ease and prevent injuries like these.
Symptoms
- Pain in area of “ball of foot”
- Burning or tingling sensation in the foot and maybe some numbness
- Cramping may also occur
- No swelling or bumps
Definitions
- Plantar Fasciitis
- A bundle of nerve endings whose covering is inflamed
- Occurs when the tissue surrounding a nerve become enlarged – thickened
- Usually a pinching of the third and fourth metatarsal bones which compresses a nerve
- Generally occurs in adults and is more common in females
Primary Cause
- Excessive Pronation
- Pronation is a normal movement of the foot, that allows the arch to flatten to a degree, which helps the body to absorb shock and adapt to different ground surfaces
- In analyzing ones gait, first contact is on the heel and outside of the foot; followed by a shift of bodyweight continuing forward, toward the arch and toes
- If the foot is weak or tired and/or the footwear is not supportive, then the arch can flatten more than normal, which is excessive pronation
- Flattening of the arch (excessive pronation) places pressure on the foot and can decrease themetatarsal arch thus increasing the chance of compression on the nerve creating a neuroma
- With excessive pronation, increased stresses can be placed on the foot
Contributing Factors
- Flat Feet
- Wearing of tight, poorly fitting shoes such as pointed, high heeled shoes
- Aggravated by prolonged standing
- Increased stress such as kneeling or ladders
- Mechanically there is too much movement of the metatarsals (long bones of the foot)
Treatment
- The 3 S’s – Stretching, Strengthening and Supporting, along with ICE and REST, have been found to be the simplest and most effective treatment for these injuries.
- Stretching of the foot and massage can help to decrease pressure between the toes and metatarsals
- Strengthening of the foot with the toe curl can help to strengthen the arch
- Supporting the foot with the proper shoe and insoles, can help prevent, improve or eliminate the vast majority of foot problems. This may be a Birkenstock sandal, with a broad base and contoured footbed, that is low to the ground and conforms to the foot. It may also be a shoe with an upper that wraps the foot and supports the arch and heel, thus limiting excessive pronation. The vast majority of footwear have more than enough cushion but very little support for the arch and heel. One of the easiest and most effective solutions is to add a simple over the counter insole that provides support for both the arch and heel.
- Make sure the shoe has enough room in the toe box.
- May need an additional metatarsal support to help decrease pressure on the ball of the foot.
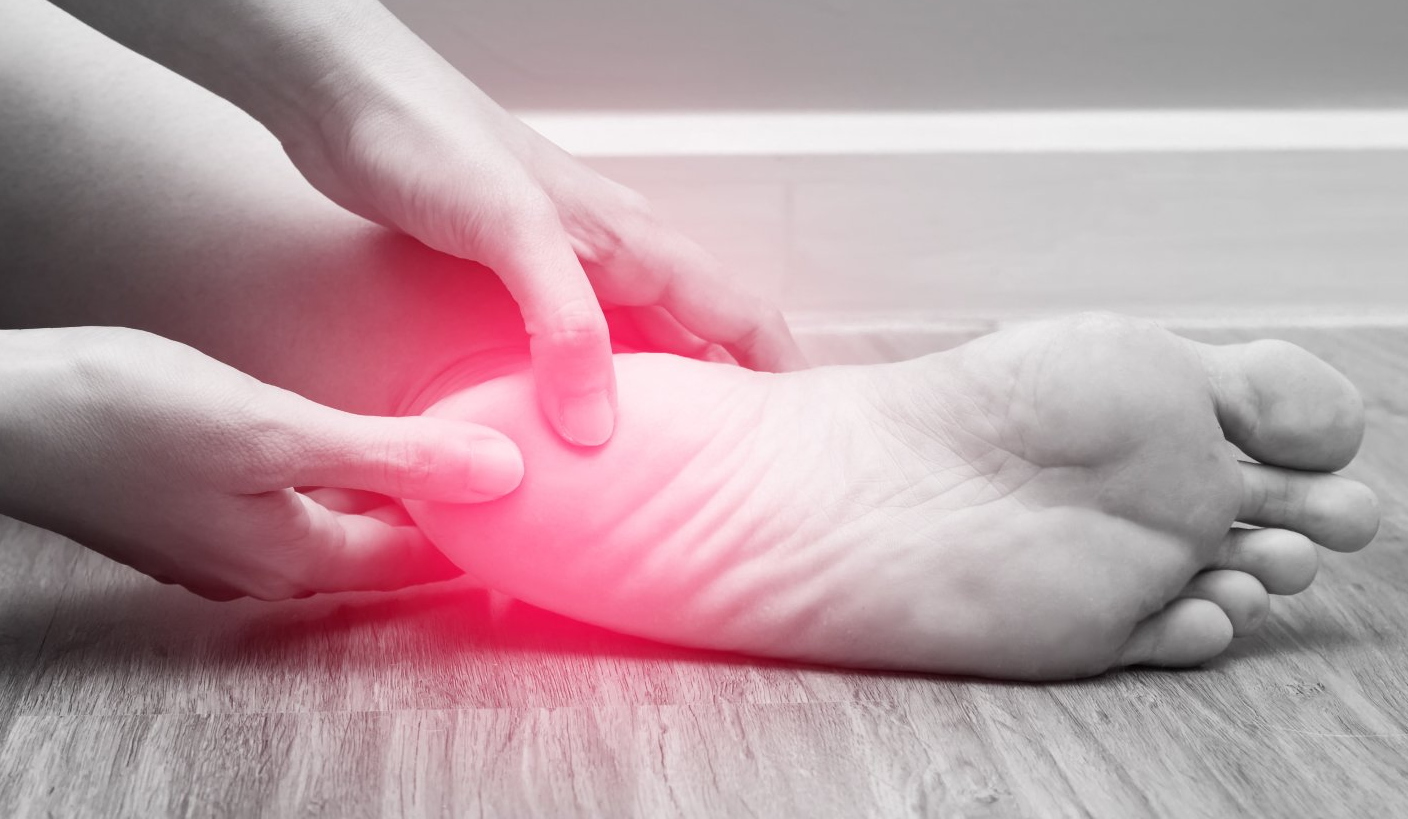
Pain in the Achilles Tendon can be caused by pronation, intense training or overuse, or poor support from your shoes. Finding a pair of shoes with good support on the inside of a shoe or in the shoe’s foundation/upper can ease the amount of stress placed on your foot and calf, thus preventing injury to the achilles tendon.
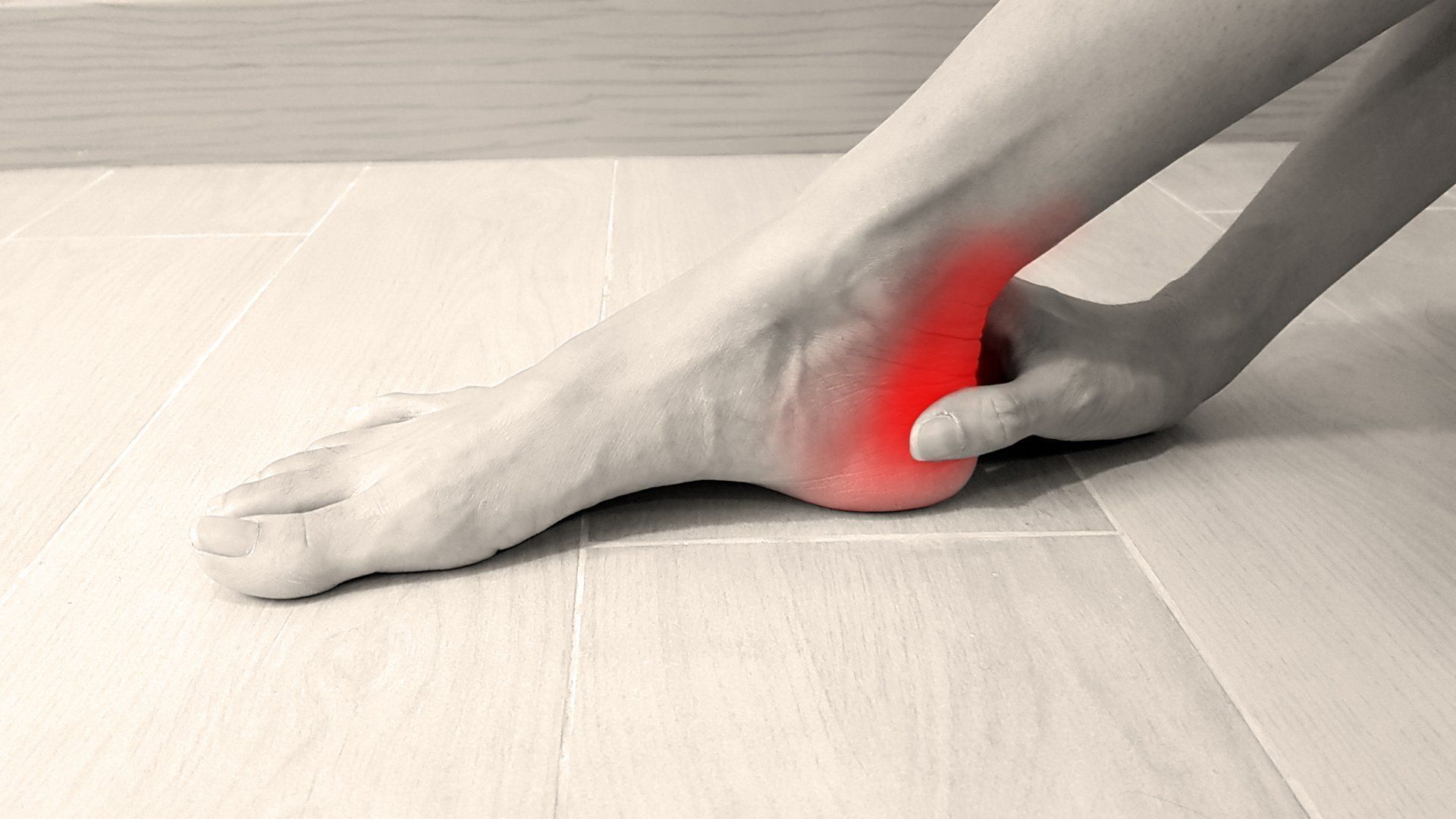
Pain in the Achilles Tendon can be caused by pronation, intense training or overuse, or poor support from your shoes. Finding a pair of shoes with good support on the inside of a shoe or in the shoe’s foundation/upper can ease the amount of stress placed on your foot and calf, thus preventing injury to the achilles tendon.